Why Are Countries Adapting To Bitcoin?
Countries are at various points in the process of adapting to bitcoin, but those choosing to adapt first may reap the largest rewards.
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency arrangement that facilitates transactions denominated in digital units known as bitcoin. Functioning since 2009, the Bitcoin network has come to dominate and even define the cryptocurrency space, spawning a legion of altcoin followers and representing an alternative to fiat government currencies such as the U.S. dollar and the Euro, and to metal currencies such as gold and silver coins.
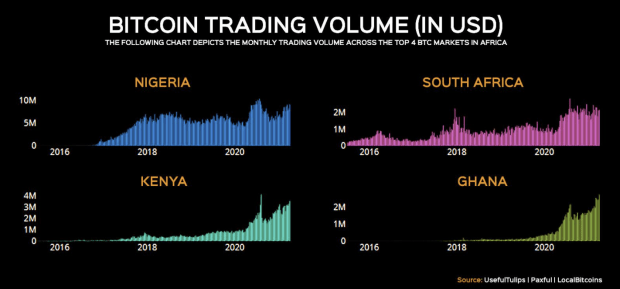
Global cryptocurrency usage has increased by 880% in the last year, particularly in Vietnam, India, Pakistan, and other developing countries. The 2021 Global Crypto Adoption Index, titled “Geography of Cryptocurrency,” compared countries’ cryptocurrency adoption based on three primary parameters: on-chain retail value transferred, on-chain cryptocurrency value received, and peer-to-peer exchange trade volumes
According to specialists from these nations, many people utilize peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges as their main on-ramp into cryptocurrencies frequently because they do not have access to centralized exchanges. Significant currency depreciation in many developing countries leads individuals to buy cryptocurrencies on peer-to-peer platforms to protect their investment value.
International transactions are also prevalent in these areas, whether for individual remittances or business use cases like buying products to import and sell. The quantity of national currency that people may move out of the country is limited. Although China was ranked fourth and the United States was ranked sixth in last year’s survey, their positions have dropped to 13th and eighth, respectively.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Bitcoin?
Advantages:
- Bitcoin users have comprehensive control over their reserves.
Traditional fiat currencies are responsive to several restrictions and hazards. Banks, for example, are flashed to economic booms and busts. As has happened in the past, these circumstances may sometimes result in bank runs and crashes. This implies that consumers do not have complete control over their funds.
- There are no costs associated with Bitcoin transactions.
Bitcoin users are not subjected to the invocation of conventional banking costs associated with fiat currencies. While fiat currency exchanges impose so-called “maker” and “taker” fees, as well as occasional deposit and withdrawal fees, Bitcoin users are not subject to these fees. This adds, amongst other things, no account sustaining or minimum balance fees, no overdraft costs, and no returned deposit penalties.
- For international payments, Bitcoin transactions offer minimal transaction costs.
Fees and currency charges are expected in standard wire transfers and international transactions. Transacting via the Bitcoin network is typically cheaper than bank transfers since there are no intermediate organizations or governments involved. This may be an essential benefit for tourists. Furthermore, bitcoin transfers are instantaneous, bypassing the hassle of usual permission methods and delivery times.
- Bitcoin transactions are entirely safe.
Bitcoin is not physical money. As a result, robbers will be unable to physically steal it. Hackers may steal a person’s cryptocurrency if they have access to the wallet’s private keys. However, stealing bitcoin is theoretically impossible with adequate protection and industry-standard practices. While there have been many other allegations of cryptocurrency exchange hacks, bitcoin transactions have remained unaffected. In conclusion, transactions offered out between two (or more) addresses are protected.
Disadvantages:
- Bitcoin is not yet accepted across the nation
Bitcoin is still only accepted by a limited number of internet businesses. As a result, relying only on bitcoin as a currency is near impossible. It’s also possible that governments may compel firms to stop accepting bitcoin in order to monitor consumers’ transactions.
- Wallets can be misplaced
One’s bitcoin is dramatically “lost” if a hard drive fails or a virus corrupts data, and the wallet file is damaged. There is nothing that can get the money back. These coins will remain orphaned in the system. This has the potential to bankrupt a wealthy bitcoin investor in a matter of seconds, with no means of replacement. The investor’s coins will be enduringly orphaned as well.
- There is no buyer protection.
When things are purchased with bitcoin, and the vendor fails to deliver the goods, there is no way to reverse the transaction. The problem can be approached by utilizing a third-party escrow service such as ClearCoin. However, escrow services would then take on the role of banks, making bitcoin more like conventional currencies.
- Technical flaws that aren’t known
The Bitcoin system may have vulnerabilities that have yet to be discovered. Because this is a relatively new method, if bitcoin were extensively accepted and a vulnerability was found, it might result in enormous riches for the exploiter at the cost of the Bitcoin economy.
How Is Bitcoin Used In Other Counties?
Since its commencement in 2009, bitcoin and the other cryptocurrencies that followed have been fraught with contention and controversies. While bitcoin has been extensively attacked for its volatility, use in illicit activities, and the amount of energy required to mine it, some people, especially in developing countries, view it with great hope amidst economic storms.
However, as many individuals turn to bitcoin as an investment, these problems have materialized in a slew of new limitations on how they may be used. The authoritative position of bitcoin varies significantly from nation to nation, with specific relationships still being established or changing often. While most governments do not make it unlawful to use bitcoin, its position as a payment method or a commodity differs, with different regulatory consequences.
Some nations have imposed restrictions on how bitcoin may be used, with banks prohibiting their clients from transacting in cryptocurrencies. Other countries have explicitly outlawed the usage of bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, imposing stiff fines on anybody who transacts in them. These are the nations where bitcoin and the state have a tense relationship. Despite this, it appears that the future may hold more countries continuing to look to bitcoin.
This is a guest post by Jacques Chirac. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.