What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a technological breakthrough rising as a new global monetary system. This article will offer you some guidelines to understand why it matters.
What Is Bitcoin and How Does it Work?
Bitcoin is an innovative technology that introduces a new monetary system, based on a peer-to-peer network of users’ nodes (computers) with no intermediaries like central banks or any type of financial institution.
For the first time in history, anyone can participate in an open network and contribute to empowering it, with no background distinction or permission required by any authority or organization.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a fast-growing evolution of money, an investment, a way out of the current unsound economic system, and a new programmable payment method. Various concepts and disciplines could be approached to fully understand Bitcoin because it can be of different utility to different people.
The various avenues will be revealed when going down the Bitcoin rabbit hole, and the journey will be captivating. With this article, you can start learning about Bitcoin’s purpose, who creates the coins, and if it is real money, including more practical advice about buying bitcoin and how to keep your coins safe.
Bitcoin is an electronic peer-to-peer cash system based on a distributed digital ledger called a blockchain or timechain. The ledger includes transactions approved by the peer-to-peer network instead of a central authority. Bitcoin (with an uppercase letter B) refers to the protocol, software, and network, while bitcoin (with a lowercase b) describes the native monetary asset.
Unveiled by a mysterious person or a group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency ever created and was described in detail in the white paper published on October 28, 2008. A digital version of cash, which in its physical form is inherently peer-to-peer, was the hardest thing to build, and the genius of Satoshi was to combine existing technology and processes to overcome the enduring issue of double-spending digital currencies without relying on a third party.
Nobody knows the true identity of Satoshi, who disappeared in 2011, leaving the project to volunteers to expand and upgrade. Therefore, it’s fair to say that Bitcoin has no single leader and can survive and thrive without a CEO. Readers who need a comparison can think more of an internet protocol, such as TCP/IP than a company.
Read More >> Exploring the origin of Bitcoin
Read More >> With Bit gold, Nick Szabo was inches away from inventing Bitcoin
Read More >> Is Bitcoin legal?
How Does Bitcoin Work?
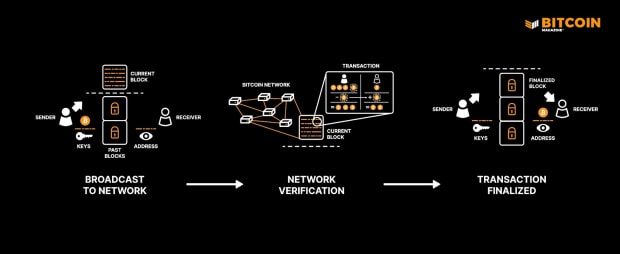
When users send or receive bitcoin, their transaction is sent to the network of Bitcoin nodes. Each node receives the file and verifies that it’s legitimate. Once verified, it’s added to the Mempool and then passed onto the other nodes in the network. The Mempool stores valid, yet unconfirmed transactions.
Miners then group those transactions together and create a block of transactions, typically selecting those transactions with the highest fees first. Each block is encoded with a block header, transaction counter and transactions, which contains supporting information about the transactions and the hashes.
Miners then compete with each other to be the first to append the next block to the blockchain. The miner or mining pool with the most computational power has the best chance of doing so, however that isn’t deterministic. Transactions are confirmed and new blocks are added thanks to a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm that requires miners to find a valid hash below a target set by the network. The successful miner is rewarded with new bitcoin as a reward for securing the network; this is known as the block reward and it’s how new bitcoin are minted.
Each block is linked to the previous block thus creating a chain of blocks that cryptographically establishes a public record of valid transactions that can’t be altered (immutable) without altering its block and the ones after it..
It’s worth noting that the protocol defines the rules and PoW determines how these rules will be followed and is regarded as one of the most secure solutions to the Byzantine Generals Problem, a more academic term for solving the double-spending problem without relying on any third party.
Users don’t need to know how Bitcoin works precisely, like they probably don’t know how the internet works despite benefiting from its use. However, it is helpful to grasp Bitcoin’s basics as this will help them understand why Bitcoin matters.
Why Is Bitcoin Revolutionary?
Bitcoin technology facilitates a trustless economic system where borderless financial transactions can be finalized without intermediaries. While traditional banking and payment systems heavily rely on trust, Bitcoin offers a way out of this system with no third party to resolve the double-spending problem and maintain properties like censorship resistance, immutability and decentralization.
Such a framework allowed the creation and implementation of a system effectively disjoined from government control, delivering a revolutionary separation of money and state for the first time in history. Bitcoin breaks all models we’re used to, starting with reduced state power and control, the exact reason governments and their affiliated mainstream media spread disinformation and FUD about Bitcoin.
Bitcoin offers real digital scarcity which makes it a store-of-value asset; censorship resistance as an assurance that everyone can use it at any time and everywhere, with no discrimination; settlement finality, which almost instantly ensures that transactions are irreversible.
Bitcoin’s settlement finality is still a widely underrated feature, while it represents a valid alternative to more traditional payment methods like Visa credit cards and SWIFT as the underlying structure of bank payments. These more conventional payment systems may take up to six months to settle, while a typical Bitcoin transaction is finalized within 10 minutes to a couple of hours.
Bitcoin’s Second Order Effects
Bitcoin’s second order effects might offer real innovation and solutions to some of the crucial issues the world is experiencing nowadays. The switch from an inflationary to a deflationary society that Bitcoin and generally all technology encourage, will increase our purchasing power, improve productivity and efficiency, and shape more cost-effective systems while creating a more equal world.
The energy sector and climate change are also being addressed by Bitcoin champions. Besides increasingly employing renewable energy, Bitcoin miners are capturing waste energy — or gas flare energy — in regions like the Middle East where oil production is considerable and gas emissions need to be contained. Bitcoin is key to an abundant, clean energy future.
What Is Bitcoin Used For?
Bitcoin’s innovative technology offers beneficial utility to every participant, from individuals to businesses. Fast and easy, mobile, global payments can be performed through a simple scan-and-pay method without needing a burdensome verification process like know-your-customer (KYC) rules typically require. A purchaser will display a QR code while the receiver only needs to scan it for the transaction to be processed and verified.
SHA-256 cryptography ensures security and control over your money, guaranteeing that funds can only be spent by their rightful owners. The energy employed by PoW prevents other people from attacking Bitcoin by rearranging the blockchain and altering your transactions.
Also, Bitcoin allows users to protect their privacy better and send transactions pseudonymously if they employ the proper measures, such as changing the bitcoin address each time they execute a transaction.
Here are some of Bitcoin’s use cases:
- Long-term savings
Bitcoin’s volatility often dissuades institutional and retail investors because they don’t assess its value in the long term. Indeed, volatility is expected and as the price grows and liquidity continues to flow in, bitcoin’s price will mature and stabilize.
Bitcoin’s volatility has captured the attention of greedy investors who contribute to its rapid price increases. They end up buying out of greed but staying for its promise, which means as time goes by, Bitcoin becomes a stable network of enthusiasts that won’t easily sell its native asset, thereby improving its soundness.
- Trading
Like every asset with value, bitcoin has become one of the most traded holdings in recent years. There are plenty of tools available for anyone who wants to start trading bitcoin, and many traders have turned it into their primary source of income by learning strategies to take advantage of bitcoin’s volatility. The common goal for bitcoin traders is not to grow their capital in fiat terms but to increase their bitcoin holdings.
- Inflation hedge
Bitcoin has grown as a hedge against long-term inflation. Unlike traditional currencies that lose purchasing power over time, the cryptocurrency has proven resistant to such market conditions thanks to properties like scarcity, increasing technological accessibility, and durability.
- Remittances
By removing intermediaries and enabling borderless payments through the Lightning Network, Bitcoin is growing as a tool to facilitate remittances. Emblematic is the growth of Bitcoin remittances in El Salvador, where the cryptocurrency was adopted as legal tender in 2021, and remittances account for 24% of El Salvador’s GDP. The country could represent a testing marketplace for international remittances in other countries.
- Collateral
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is an emerging and fast-growing branch of finance used to secure mortgages, refinancing, and other services where bitcoin can be used as a collateral asset to secure funds in different currencies or assets. While this is still a grey area for many who offer traditional financial services, bitcoin as collateral is already operative and widely used by cryptocurrency supporters.
- Payments
Layer 2 (L2) protocols have been created to tackle the scalability issue and offer faster and cheaper off-chain payments than Bitcoin’s base layer (L1). The best two examples that have been developed are the Lighting Network and the Liquid Network, both built on top of Bitcoin and offering the same robust decentralized security paradigm.
- Energy monetization
A monumental breakthrough in energy production is happening right before our eyes. What has typically been seen as a huge problem due to excessive mining power consumption is becoming an advantage for Bitcoin.
The idea is to exploit excessive renewable sources of energy production, monetize the surplus supply of the power output and make the project cleaner and more cost-effective. Bitcoin miners are particularly fitted for such a scheme since they can move and settle where the power is, even in remote areas, to fill gaps, thus driving a clean energy transition.
It’s a win-win situation for the miners who get plenty of cheap energy and for the energy providers who manage to sell surplus electricity that would go wasted otherwise.
Is Bitcoin A Safe Investment?
Pros
- Bitcoin is considered a safe investment primarily because, over time, it has become highly secure thanks to its SHA-256 algorithm, which was designed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA). No other cryptocurrency can claim the same security; Bitcoin’s blockchain has never been hacked, and as time goes by and blocks are added to the chain, it becomes increasingly difficult to attack.
- Bitcoin’s supply and issuance are programmed by protocol and this predictability is an important feature. So as long as supply/demand economics upholds, the properties of scarcity should prevail.
- Bitcoin is also unique and secure as private property because once you own it and store it properly, it cannot be taken away from you. It doesn’t rely on a local authority or legal system to protect it; instead, it’s secured by the natural incentives of those participating in the network. Bitcoin investors should also consider that their bitcoin is safer in their Bitcoin wallet than their cash is in a bank where it is rehypothecated.
- If we consider the Lindy effect, according to which the life expectancy of a technology is proportional to its current age, then Bitcoin can be expected to exist for at least another 12 years. Moreover, despite being declared dead hundreds of times in the past, Bitcoin appears to be here to stay, and we can expect it to live much longer.
- Public personalities, influential investors and entrepreneurs would not have gone as far as endorsing it if they did not believe Bitcoin was here to stay. Jack Dorsey, Elon Musk and Tesla, Michael Saylor, Ray Dalio, and several other VIPs have added Bitcoin to their companies’ reserve assets, often replacing gold and cash reserves, besides owning the asset in their personal portfolios.
Cons
- Price volatility is often seen as a significant issue to potential bitcoin investors, but many will argue that’s actually a feature, not a bug. To start with, bitcoin is still a relatively new asset and, as such, is prone to substantial price swings. Price volatility has reduced over time and this trend is expected to continue as bitcoin matures. Moreover, bitcoin’s fluctuations are only short-term, and the price tends to go up in the long-term, especially if we consider a multi-year chart where the uptrend becomes apparent.
- Technical barriers are normal for new technology and Bitcoin’s learning curve can be daunting for newcomers. However, using wallets, keys, apps, and all accessories becomes easier with time and thanks to companies’ contribution to better usability.
Read More >> Common misconceptions about Bitcoin
How Does Bitcoin Make Money?
Bitcoin’s network fulfills well-designed incentives that ensure miners are rewarded with bitcoin to keep it alive.
At first, Bitcoin was mined by regular node operators who simply employed their computer central processing unit (CPU) power to find the next block, in the same way that Satoshi mined the first blocks. Node operators were incentivized to use their electricity to expand the network by adding new blocks to the longest chain and being rewarded with bitcoin.
This process is called proof of work, and it’s the essential consensus algorithm that constitutes the backbone of the Bitcoin network and provides it with the highest security.
As new nodes joined the network and started to compete to receive block rewards, the standard CPU power was no longer enough. Over ten years, miners had to switch from graphic processing units (GPUs) to the current application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) mining devices to compete with other miners and find the next block faster.
In essence, through such an incentivizing system, this is how Bitcoin makes money. How much does it cost to produce one bitcoin? Several elements must be considered to assess if mining is profitable, from the cost of electricity to the mining difficulty (an automatic adjustment necessary to keep the block generation time at about 10 minutes) and the block reward.
It is estimated that with a block reward of 6.25 BTC, difficulty at 27.5 trillion hashes, $0.15 per kilowatt hour (kWh), and energy efficiency of 45 joules per terahash, the cost to produce 1 BTC is about $35,500.
Read More >> Why Proof of Work is a superior consensus mechanism
Read More >> Making The Decision To Mine Or Purchase Bitcoin
Ok, So Bitcoin Is Similar To Gold?
Bitcoin has similar monetary properties to gold and is often addressed as digital gold. The process for producing gold and bitcoin are similar. Gold is mined and extracted from the ground using energy-intensive machinery, while new bitcoin are mined using energy-intensive computers. The mining process they both go through is what associates them, along with rising marginal costs, a consequence of more parties wanting to mine making mining more difficult to achieve.
This means that mining is an expense that cannot be forged, a concept known as unforgeable costliness that cryptographer and computer scientist Nick Szabo explains.
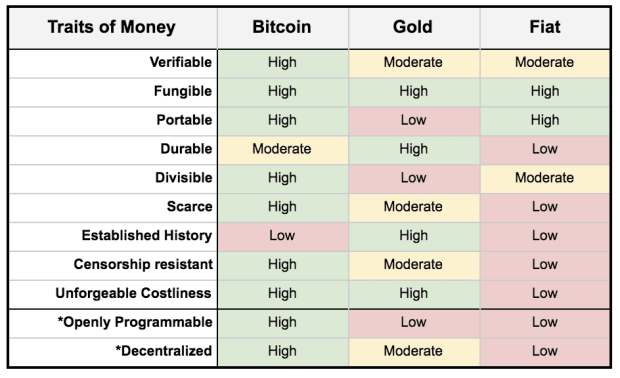
Both bitcoin and gold are scarce, yet nobody knows the overall supply of gold, while we know there will only be about 21 million bitcoin in circulation. Bitcoin can be easily verified and audited due to its primarily immutable and programmable protocol, compared to physical assets like gold which are much harder to scrutinize. Like gold, Bitcoin is decentralized money that can be held independently from any intermediate.
Both bitcoin and gold are often referred to as hard money, which is something everyone would like to retain because it’s robust, reliable and secure. Compared to gold, bitcoin is already better hard money because of its divisibility and portability properties that allow the cryptocurrency to be more easily managed and transferred.
Read More >> Bitcoin vs gold
So, Is Bitcoin Money?
From the use of commodities like grain to precious metals like gold and subsequently government-controlled fiat currencies, money has been perceived as a means that facilitates value exchanges between participants of an economy.
Over time the definition of money has shifted to include a few main properties like fungibility, durability, portability, divisibility, and stability, all applicable to bitcoin, except stability for now.
If we add scarcity and other properties like censorship-resistance, programmability and decentralization, bitcoin is close to the most perfect type of money ever created, as highlighted below.
While we’ve been led to believe that only fiat currencies are money, this wasn’t the case until 1971, when U.S. President Richard Nixon decided to default on the U.S. dollar convertibility to gold.
Nowadays, our money is digitally conceived, and what we check in our bank account, for example, is a simple entry on the bank ledger. We don’t even know if any real money is actually held on the other side of the ledger.
Bitcoin represents the purest form of money, without the physical attribute. While it is also an entry in a ledger, if we use a non-custodial wallet (not managed by a third party but ourselves), we own access to it through the private key, and nobody can take that money away from us. This is why Bitcoin helps refugees escape wars, and authoritarian governments when the local fiat currency is made unavailable by a nation state that can freeze assets unchallenged.
Read More>> Understanding Money Is Key To Understanding Bitcoin
Read More>> What is happening to money?
Read More>> The monetary properties of Bitcoin
Is Bitcoin A Good Investment?
With an asset increasing in value as fast as bitcoin, such a question is unavoidable. Looking at bitcoin’s price development, it’s clear that there have been several extreme bubble phases with subsequent massive price drops.
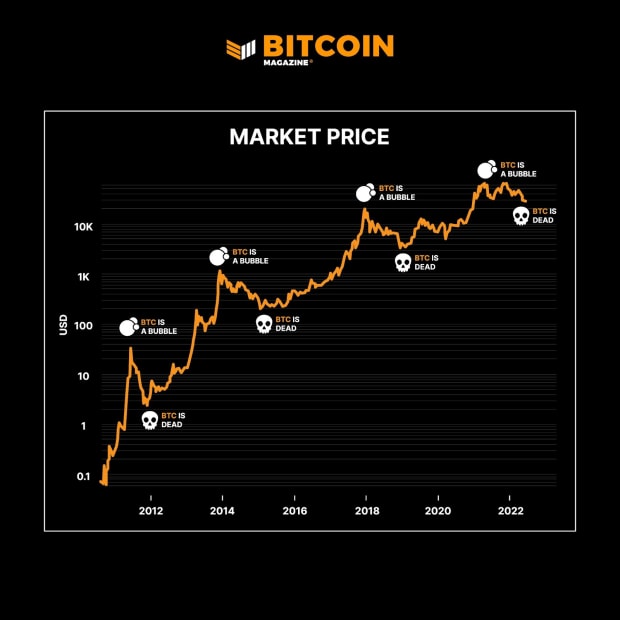
Despite the enormous growth bitcoin has recorded over the years and its price reaching an all-time high (ATH) of nearly $68,000 in November 2021, bitcoin’s potential to grow further is very strong — often referred to as Number Go Up (NGU) technology, strictly liaised with Bitcoin’s halving event that cuts block production in half, making it more scarce and, therefore, more valuable each time.
When bitcoin hits a new ATH, new potential investors are inclined to believe it’s too late to invest in bitcoin because the price is already inaccessible. However, bitcoin’s price has always proved them wrong by growing higher every time.
Should bitcoin reach $100,000 or $1 million, then people won’t mind if they bought bitcoin at $2,000, $20,000 or even $60,000. The important point is that you bought bitcoin and participated in the capital gain. Obviously, should that scenario happen, the more bitcoin you have, the better.
Financial institutions and banks alike are increasingly offering bitcoin in investment portfolios, suggesting bitcoin is not going anywhere and gradually but steadily moving up in market cap ranking compared to gold, for example.
Considering that fiat currencies continue to lose purchasing power and bitcoin, in contrast, continues to show resilience to market conditions increasing in value over the years, investors can quickly draw their conclusions.
It is always good practice to understand an asset you decide to invest in, and this article should offer you the essential information to assess if bitcoin is worth your investment.
It’s A Bit Expensive, What about The Cheaper Coins?
A cheaper asset does not correspond to better value. This is a concept that many crypto investors have come across unfortunately by losing their money in shady projects they invested in because they were cheap.
The rise of coins alternative to bitcoin (altcoins) has opened the door to additional investment assets in the cryptocurrency space. Bitcoin is seen as already too expensive to buy, so new investors are inclined to put their funds in altcoins which, in their opinion, have higher growth potential. This strategy has repeatedly been proven wrong, and new investors have often lost money because they invested based on a price rather than the solidity of a project.
Be careful to not be fooled by this unit bias, which is the concept that we are more enticed to buy a whole unit of a given currency instead of a fractional quantity. Many newcomers hold the irrational view that BTC is too expensive and hence look into “cheaper” alternative coins that they can own more units of.
The extreme speculation that occurs in crypto markets has led small investors to buy the cheapest of coins because they believe they will go up in value regardless of their real use case and fundamentals. This leads them to make much riskier investments and buy and HODL altcoins.
Altcoins have shorter life spans than bitcoin and are, therefore, less secure. They are often promoted as higher-return investments than bitcoin in fiat terms but against bitcoin are a disappointment. They have none of the properties that make bitcoin so valuable, starting from their circulation supply, which is often difficult to assess and usually unlimited.
They are decentralized in name only (DINO) but are generally controlled by an influential leader, a group of developers or venture capital firms and provide a type of governance that makes that decentralization difficult to confirm.
Besides being a better asset, bitcoin is highly divisible, which means a fraction of a bitcoin can be acquired. As little as $100 currently buys approximately 100,000 sats (BTC 0.0032), the smallest fraction of a bitcoin. One satoshi is 0.00000001 BTC, and if bitcoin continues to grow, sats will be the new standard means of exchange, and it makes sense to start accumulating them if one cannot afford a whole bitcoin.
Can Bitcoin Be Converted Into Cash?
While investors should be aware that turning bitcoin into cash may trigger a taxable event and could be a regrettable decision over time, it is undoubtedly possible to exchange it for cash in a few different ways.
- Using cryptocurrency exchanges, which are third-party brokers, is the most popular way to move your bitcoin out of a wallet and turn it into cash. The operation requires a few KYC steps to verify your identity and comply with money laundering regulations before you can even link a bank account to transfer the relevant fiat currency bought with the sale of bitcoin.
- Bitcoin Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), also called Bitcoin Teller Machines (BTMs), are another way to cash out your bitcoin, and there are roughly 38,000 worldwide. It’s as easy as scanning a Bitcoin wallet QR code over the device to sell your bitcoin for cash; however, the fees using BTMs are much higher than those through nearly any other method.
- More recently, banks have considered offering bitcoin. Especially in the U.S., a few major financial institutions are apparently ready to allow their customers to buy, hold or sell bitcoin. The increasing interest of customers around Bitcoin encourages them to follow this path, knowing that otherwise, they would look elsewhere to invest in bitcoin.
- Among the fintech services that banks are rolling out for Bitcoin, there are debit card rewards paid in bitcoin and new types of bank accounts that may pay interest in the cryptocurrency.
How Much Should I Invest?
Taking into account that it’s never wise to invest more than you can afford to lose, how much to invest in bitcoin is entirely based on the individual’s availability and preference. Even the most secure investments bear a certain risk, and bitcoin is no exception.
Learning about Bitcoin would help build trust in it, and starting with small purchases can offer some familiarity with the asset.
Bitcoin is one of the favorite acquisitions of small retail investors who have learned to spend less on futile things and save such money to buy bitcoin instead. Setting up regular purchases can help overcome the fear of too much volatility and better cope with its price swings. Remember to always set money aside for a rainy day.
When Is The Best Time To Buy?
Timing the market correctly is always challenging; for that reason, the best time to buy bitcoin is when you have money available to invest.
Fundamentals and technical analysis can help assess if the price is too high; for instance, when bitcoin reaches an ATH too quickly, it will likely retrace. The opposite is also true, so buying bitcoin when it dips is always a good idea if the investment is for a long-term period, knowing that the asset can go lower.
The best and favorite strategy of bitcoiners is to dollar-cost average (DCA), which means you allocate affordable money daily, weekly or monthly. This way, price swings won’t matter, and the difference can’t even be perceived with small purchases. Yet, the strategy allows you to accumulate a decent amount of bitcoin over the long term without feeling much of a burden.
Lastly, Keep Your Coins Safe
All the knowledge about Bitcoin and finally buying it are helpless if you don’t secure it. Remember, because of Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, there won’t be a call center or helpdesk to assist if you have problems with its management.
That said, it is relatively easy to safely store your bitcoin if you follow a few essential steps.
The first rule is to keep your bitcoin out of exchanges. These should only be used for cash conversions; thus, a non-custodial wallet is recommended instead. With Bitcoin, you are your own bank and should always secure your private keys. As a traditional Bitcoin mantra says, “not your keys, not your bitcoin.”
The best and most secure wallets are held in cold storage, which means offline. A private key should never, for any reason, be stored in a computer or the cloud. Online transactions and hot storage (always online) have a much higher chance of being hacked, and you can potentially say goodbye to your bitcoin.
Conclusion
Taking full ownership and control over our finances through Bitcoin requires the willingness and personal responsibility to learn what Bitcoin is, its purpose and its promise. Certain concepts might be a little complex to grasp at first, but with the passing of time it will prove to be a worthwhile endeavor. Not only has Bitcoin the potential to increase a person’s financial wellbeing, but can also genuinely reshape the world and make it a better and fairer place.
You will then understand why it’s viewed as the next logical step in the evolution of money, a step that takes — actually re-takes — money out of the hands of governments. It’s for this reason that the media and authorities spread so much fear and mistrust in Bitcoin, but it’s also the reason why we, as HODLers, believe it brings so much hope for humanity.
Follow Bitcoin Magazine on Twitter to learn more about Bitcoin and start earning some sats by taking the 21 days to learn bitcoin course to continue your learning.