What is a Wallet? Guide to storing Bitcoin
After you receive bitcoin, you’ll need to store it in a secure digital wallet. This guide helps you understand what a wallet is and how there are different wallets to suit your needs.
A wallet is where you typically store your bitcoin after purchase, just like a physical wallet is used to keep your cash and cards.
Once you understand bitcoin and are ready to buy it, earn it or receive it as payment in exchange for goods and services, you should set up a wallet so that your counterpart has a digital address to send the bitcoin to.
Your wallet must also be secure and robust for storing your bitcoin. Nowadays, there are plenty of digital wallets to choose from and this guide offers comprehensive information to help you make the right choice.
Wallets can be hardware-based or software-based, can be downloaded on a mobile device, on a computer desktop or stored on paper by printing a QR code that enables access to the private keys.
WHAT IS A BITCOIN WALLET
A bitcoin wallet is an electronic device that allows you to send, receive and access your funds, similar to how a traditional wallet stores your banknotes or coins. In contrast with a physical wallet, a bitcoin wallet does not store actual coins but the private key — cryptographic data — that proves ownership and gives access to the actual money that is held on the blockchain.
Losing the private key or having it stolen is a Bitcoiner’s worst nightmare because it means the funds are lost. This is why securing this cryptographic data is the first thing you need to do when you acquire or receive bitcoin. Your private key could also be lost through hacking, phishing, computer malfunctions or the loss of the device itself.
In light of what happened to Celsius, Voyager, Three Arrows Capital and FTX in 2022, when they lost all their customers’ bitcoin through poor business practices, leading to their bankruptcies, the case for self-custody could not be stronger. While these bankruptcies were a difficult pill to swallow for the cryptocurrency industry, they were not Bitcoiners’ first rodeo with bankrupt exchanges, for the Mt. Gox hack in 2014 led to the initial movement of “not your keys, not your coins,” which has continued to this day.
Bitcoiners often refer to themselves as sovereign individuals. To be a sovereign individual, you must take self-custody of your BTC. To do this, you must learn about wallets.
WHY USE A BITCOIN WALLET
“Not your keys, not your coins” is a powerful Bitcoin mantra, meaning if your wallet doesn’t give you exclusive access to your private keys, you don’t actually own bitcoin. Instead, a third party — like an exchange — will hold it for you just like a bank keeps custody of your money.
Bitcoin was created to offer an alternative to the banking system so your wallet will give you financial sovereignty without intermediaries, protection from rehypothecation and the ability to store your wealth safely.
Bitcoin teaches you to take personal responsibility for your money, resulting in you storing your BTC safely and spending it wisely. One of the first things you must learn while exploring this path is how wallets work.
HOW DO WALLETS WORK
The Bitcoin timechain — also known as a blockchain — is a shared public ledger where all bitcoin value transfers are conducted through bitcoin wallets. The wallet’s private key is your go-ahead to use your coins, the authorization and verification that you are the rightful owner of the bitcoin in your wallet. It’s like the password that allows you to enter your online banking.
Private keys are 256 digits long, making them impractical for storing, transacting and securing your money. This is why they are protected in a bitcoin wallet that will automatically activate them for transacting, in pair with a public key.
When you create your bitcoin wallet, a seed or recovery phrase is automatically generated to retrieve your funds in case you lose access to your private key. A seed, mnemonic or recovery phrase is a succession of 12 or 24 words that will be used to generate any Bitcoin key you need to send and receive bitcoin.
Such wallet setup is homogeneous across the board, but different wallets exist to satisfy various requirements and preferences.
There are many types of bitcoin wallets, depending on your requirements. You should be aware that they all present some level of risk — in particular custodial wallets that third parties control. We recommended that you follow the guidance below to avoid costly mistakes and risk losing your funds:
- Don’t use a wallet that doesn’t give you recovery data.
- Don’t use a paper wallet unless you’re an advanced user and recognize the risks involved.
- Large amounts of bitcoin should preferably be stored in multisig wallets.
- Remember to set up recovery instructions for your heirs.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF WALLETS
Mobile wallets
Mobile wallets are apps like Bitcoin Wallet and BlueWallet. They are convenient portable tools providing a QR code for quick face-to-face transactions. Some even use near-field communication (NFC), allowing users to tap their phones against the merchant terminal without providing ID verification.
They come with significant risks as they are the least secure, given how easy it is to lose your mobile device. You can still restore your wallet on a new phone if you hold the private keys; however, due to their online reliance, you can lose access due to hacks that can lead to losing your funds. For this reason, they are best recommended for small transactions and are not suitable for storing large amounts of bitcoin.
Using two-factor authentication (2FA) for extra security, preferably an authenticator app like Google Authenticator, makes the wallet less vulnerable to hacks or sim-swap attacks.
Web wallets
Web-based wallets are usually exchange-based wallets like BitGo or Blockchain.com that let you store your bitcoin and make transactions. They are considered hot wallets because they are online websites that need an active internet connection.
Users’ private keys are stored on the provider’s server, which makes them highly vulnerable to hacks or confiscation if something goes wrong with the exchange. It is highly recommended to avoid storing the majority of your bitcoin in a hot wallet.
Desktop wallets
Desktop wallets, like Atomic Wallet and Electrum — one of the original bitcoin web wallets, around since 2011 — are open-source programs that can be downloaded on your computer and store your private keys on your hard drive.
While they are generally more secure than mobile or web wallets because you aren’t trusting third parties to hold your coins, they are still vulnerable to hacks through an internet connection.
Cold Storage wallets
Cold storage wallets are any form of wallet that live on a device that is not connected to the internet. Offline connection protects the wallet from any form of internet-based attack.
Hardware wallets and paper wallets are your typical cold storage solutions. There’s also deep cold storage, which is any cold storage wallet buried deep in the ground, secured in a vault or any such method so as to ensure your bitcoin is considerably more inconvenient to access than it otherwise would be.
Hardware wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices, like USB drives, that store your private keys offline. They are not connected to the web and are usually considered very secure since computer viruses or online hacks cannot attack them.
Setting them up requires some technical skills, but the manufacturer usually provides a step-by-step guide that is easy to follow. Try the wallet with little money first to gain experience and feel more secure running a transaction. Only load it with bitcoin once you are confident enough to transfer significant money.
Always make sure you’re purchasing the hardware wallet from an original manufacturer like Ledger, Trezor or COLDCARD, as fake wallets retrieved in marketplaces like Amazon or eBay will steal your bitcoin.
Paper wallets
Paper wallets are also considered cold storage, requiring you to store your private keys offline on a piece of paper that you print out as a QR code. These can be quickly scanned to add the keys to a software wallet to make a transaction.
They are rarely used nowadays due to the abundance of alternatives, but they are very secure since no hacker can access and steal the passwords. They are also very private since there can’t be any dissemination of personal data on the internet.
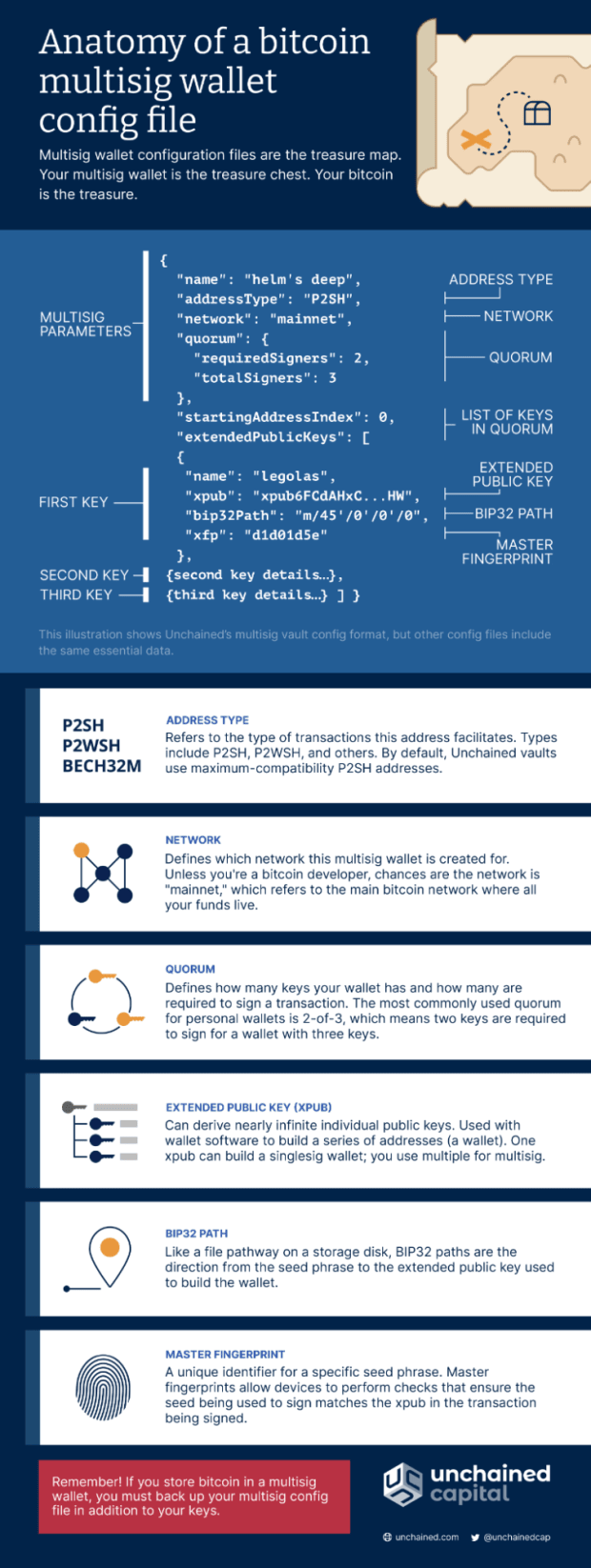
Multisig wallets
A multisig wallet will require more than one private key to sign and authorize a bitcoin transaction, adding an extra level of security. It means that a number of people, generally two out of three (or three out of five), must approve a transaction limiting the chances that a hack or theft happens, which single-signature wallets are more vulnerable to experience.
The transaction is finalized once the required signatures approve it. There’s no hierarchical order among the signatures required; only the number of signatures per setup is needed.
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN CHOOSING A WALLET
Bitcoin-only Wallet or Multicurrency Wallet
Every cryptocurrency wallet will let you store bitcoin, but only some bitcoin wallets will let you store cryptocurrencies other than bitcoin. If you are focused on sound money with no distractions from other cryptocurrencies, consider the options we provide here and just focus on a secure bitcoin-only wallet that grants you control over your private keys.
Research Wallet’s Reputation
Bitcoin Magazine endeavours to provide you with tutoring on the most trusted and reliable bitcoin wallets in circulation; however, plenty of material on the internet offers you a clear understanding of the different wallets and their reputation. Software engineer and Bitcoin advocate Jameson Lopp, for example — who is also CTO and co-founder of leading self-custody solution Casa — provides some of the most reliable and comprehensive educational material related to Bitcoin on his personal website.
Research Wallet Backup Options
It can never be stressed enough that backing up your wallet should be a priority. The fundamental recovery option you have is to back up your private keys securely by writing down and storing your wallet seed phrase in a safe physical location that you remember.
Never do this online, not even on the cloud or your computer, where your funds are always at risk that hackers could steal them.
Research Key Management
Private key management is an essential component of your wallet; think of how your bank account is protected and you’ll get the idea. Learn if your private key has an automatic cloud backup or a manual one; if your wallet lets you store your keys externally or on the same device as the wallet application; if multiple independent keys manage it.
Understand the purpose of your wallet
Consider what’s most important to you when choosing your wallet:
- Convenience: do you need a wallet for daily transactions, for mobile use or trading?
- Security: this should always be your priority, regardless of a type of wallet.
- Anonymity: some wallets are more privacy-focused than others. Wasabi Wallet & Joinmarket offer high levels of privacy.
- Long-term investing: A wallet to store bitcoin as a long-term investment.
- Gifting: a wallet like Opendime which is suitable for giving bitcoin as a gift without revealing the private key.
HOW TO SET UP A WALLET
Setting up a bitcoin wallet is easier than it sounds and most devices are user-friendly and suitable for beginners. In most cases, it’s easy to follow the device’s instructions as you go through the process. However, below you can find the typical procedure of setting up a wallet:
- Download and install the software, mobile or desktop wallet from the provider’s website only. You’ll need to follow the manufacturer’s instructions to set up a hardware wallet.
- Use the device’s instructions; they’re usually easy to follow. Once you download the app or the software, you’re typically ready to use it.
- Secure your private key by writing down your recovery phrase, so that you can restore your wallet should you ever need to do so;
- Transfer only a small amount of bitcoin first to get some wallet practice.
Read More >> How to set up a Bitcoin wallet
Security risks when using a Bitcoin wallet?
Bitcoin wallets are a popular way to store and use your bitcoin. However, like all digital devices, they are susceptible to security risks. Some of the most common security risks associated with bitcoin wallets include the following:
- Theft: If someone gains access to your wallet, they can steal your bitcoin. So keep your wallet(s) in a secure and safe place at all times.
- Coercion: you may be physically coerced to hand over your stack (this is called a $5 wrench attack), which may be avoided with multisig and cold storage solutions.
- Hacking: bitcoin wallets can be hacked, which could result in the theft of your bitcoin. Hacking can occur in different ways, including phishing and brute force attacks.
- Malware: Bitcoin wallets can be infected with malware, which are programmed to steal your bitcoin. So ensure your Operating System is clean and virus free.
The most secure way to store your bitcoin is to use a hardware wallet in conjunction with a multisig solution. This is the approach you should take for the majority of your bitcoin or those that you intend to HODL for a long duration.
How to make your wallet more secure
When a bank holds your money on your behalf, the bank is responsible for protecting it so you don’t need to be concerned about the threat of a robbery, fire, flooding or any form of loss.
When you own bitcoin and you take personal responsibility for safeguarding it, you become your own bank and you inherit the same concerns that any bank manager or bank security professional would have. The onus falls on you, and you alone, to protect your wealth.
Luckily, there are many options available to us in the form of wallets which help us secure our investment. Some wallets safeguard your bitcoin more than others, so it’s essential to do your research before choosing one. Here are further measures you can take to make your wallet more secure.
Store your seed phrase safely
If you want to keep your seed phrase safe, it’s essential to store it in a secure place. You can take a few simple steps for more peace of mind: you can keep it on a piece of paper, in a cryptographically secure safe or on a metal plate like the ones provided by Coldbit or Blockplate.
Keep it hidden from others, and don’t tell anyone your seed phrase. Split the seed phrase in two for further protection and keep them separate. Be creative with your Bitcoin security, as long as you remember where and how to recover your funds!
Add 25th word
When setting up your wallet, the system recommends you safely store your seed phrase, which is typically a series of 24 words. Some wallets allow an additional phrase, the purpose of which is to further encrypt your root seed. If your 24 words are compromised, the person holding those words will unknowingly need the 25th word in order to access your root keys. This solution buys you the time to swap wallets, should you need to.
Use a multisig system
Using a multisig system is one of the best safeguards for your bitcoin. There are two types of multisig solutions: hosted — like Casa and Unchained, that hold the private keys for you — and unhosted where you inherit full control, and each version has their advantages and disadvantages.
Decoy passphrase
A decoy passphrase is a system used to protect password databases, allowing hackers to believe they have cracked the file, only to be given valid credentials which do not provide access to the private keys. Cybercriminals will still be able to crack that file; however, the passwords they will get back are fake or decoy passwords.
Use more than one wallet
Using more than one wallet and spreading your funds across them may reduce the chances of losing all your funds from one point of failure. Make sure you apply all of the security measures discussed above to all of your devices to strengthen their accessibility.
Access from a secure computer
Reduce your computer’s chances of being hacked and your funds stolen by using a device only dedicated to bitcoin management. It is worth it, as overused computers are more liable to pick up malware, particularly those with weak OS security.
Use in conjunction with a full node
Using your wallet with a full node represents the ultimate protection measure you could take to secure your funds. Moreover, running a full node strengthens the network, benefiting all Bitcoin users.
Using a node protects you against fraudulent activities: no rule breaker can affect your funds since you’re using a decentralized tool that allows you to act in a trustless environment. Make sure your lightweight wallet allows you to configure how to connect to your own full node.
INHERITANCE PLANNING
Nobody likes to think about leaving this world or being incapable of managing their money one day; however, you may have wondered what happens to your bitcoin when you die? If you’re managing your own Bitcoin keys, you’ll need to plan how to pass them on to your heirs.
Owning your own keys and being your own bank already requires a significant level of responsibility and thinking about your succession too might be discouraging for some. The first thing you should do is talk to your solicitor and create a will, so that the executor can pass down the knowledge of what you intend to do with your BTC.
There are typically two ways of dealing with the inheritance of your bitcoin, although they both require some legal assistance for peace of mind:
- Manual method: You’re likely the knowledgeable person on this subject matter, so in addition to the private keys, you’ll need to pass on to your heirs the instructions explaining what to do with the private keys. The keys should be kept with trusted family members, a legal team or preferably a combination of both. It’s advisable to not provide full access to any one party, to ensure no party ever has complete control or premature control.
- Paid for service: Service providers like Casa, can work with you to create an inheritance plan that allows your heirs to access your bitcoin at the right time, with the help of a legal and technical team that can unlock the funds for your beneficiaries.
You can also find a lot of useful tips on planning inheritance processes in a book called “Crypto Asset Inheritance Planning,” written by American attorney and entrepreneur Pamela Morgan, with the technical supervision of Bitcoin educator Andreas Antonopoulos.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Where can I buy a hardware wallet?
Always buy your bitcoin wallet from the most secure source, which is the device manufacturer or the official seller. Never buy from marketplaces like Amazon or eBay, as the device may be compromised — even if it appears new — and your funds may be stolen. It’s always best to spend more and secure your funds than regret not going the safe way to acquire a brand new wallet.
What is the best Bitcoin wallet for international people?
Most bitcoin wallets are available worldwide because they are open-source and decentralized devices. Wallets like Electrum, Blockstream Green or the hardware types are available to download or buy from most countries; therefore, picking the best international wallet means choosing the most suitable device for your needs.
How much does a Bitcoin wallet cost?
Most mobile or web wallets are free. However, if you want to invest in cold storage, the cost can range from $60 for a Ledger Nano S to over $200 for the extra secure Trezor Model T.
How do I set up a bitcoin wallet with no ID?
Most bitcoin wallets do not require ID verification. When buying a hardware wallet, you must provide details to receive the device. It is recommended to use creative ways to circumvent dispatch of your physical address or even your name, email and telephone number.
For example, the least you can do is provide a generic delivery address of a store near you (or not) that could receive the wallet as a service. You can even alter your name slightly, but the store may ask for proof of identity, so keep that in mind.
How long would it take to crack a Bitcoin wallet?
The good news is that if you use all the mentioned measures, it will be nearly impossible to crack your bitcoin wallet. If you use a web or mobile wallet in what’s called hot storage, your funds are at risk. If you’re using hot storage, make sure you use the most robust password possible.
It’s been calculated that a four-digit pin code takes as little as five milliseconds to crack, while the longer your password is, the better. Twelve random letters would take two centuries to crack with today’s technology.
Can law enforcement seize a bitcoin wallet?
Yes, they can. Though it depends on the type of wallet and the security precautions taken.
Hot wallets or wallets hosted by centralized service providers are the highest risk, as law enforcement agencies could easily crack a bitcoin hot wallet or persuade a centralized service provider to provide access to the private keys to freeze — or seize — your bitcoin.
A cold wallet device could be seized by authorities but, unless you provide them with the private keys, the password and recovery seed, that device is useless and they won’t have your bitcoin.
A multisig wallet, instead, is again your best protection against seizure because, even under coercion, you would not be able to provide the full set of keys to access your bitcoin. This is especially true if your keys are kept in separate locations or held by different entities.
Read More >> Bitcoin privacy and security guide
What happens If I forget my wallet password?
A wallet password can be retrieved or reset. It’s the private key you must be careful to keep secure at all times, as if you forget it or lose access to it, you may lose your funds.
IN CONCLUSION
Your wealth is at stake if you don’t protect your bitcoin and robust, secure and non-custodial wallets are the way to do it.
Generally, small amounts of bitcoin can be stored anywhere if you’re looking to trade or spend them. However, for more considerable amounts, multisig wallets in cold storage, used with a full personal node is the ultimate level of protection you can provide to your bitcoin.
Bitcoin wallets have been in the spotlight recently with governments, like the EU, trying to ban them or at least limit their privacy and autonomy from third parties. While Bitcoin cannot be banned or censored, its decentralization and sovereignty could be compromised by persecutory activities enacted by authorities.
With everything that’s been happening in the cryptocurrency industry for years, from a regulation standpoint to criminal activities, exchange hacks and so forth, Bitcoin is widening the gap with “crypto” and finding its own ethical stance supported by companies that are only involved with its monetary soundness.
It’s never been more important to take personal responsibility and custody of your bitcoin seriously, and learning how to secure it is that little extra effort that needs to be made to reduce the risk of parting from the most powerful asset you’ve ever held.






![[promoted] FlipNpik’s Social Media Model: Boosting Incentives For Local Promotions](https://www.lastcryptocurrency.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/1777/promoted-flipnpiks-social-media-model-boosting-incentives-for-local-promotions.png)