Security vs. Utility Tokens: The Complete Guide
Ever since the invention of Bitcoin, hundreds of new cryptocurrencies and tokens have emerged to operate as digital currencies with blockchain ecosystems designed to solve specific problems for people around the world.
As with any industry, there are different categories that have been created to distinguish different types of coins.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Litecoin are primarily designed to function as currencies for everyday spending. Then we have tokens, which are split into 2 primary categories: Security and Utility.
What are Utility tokens?
Today, utility tokens are currently the most popular form of tokens. This is due to the mass wave of blockchain startups that have emerged in the past year. These startups have raised money through initial coin offerings, which require them to create their own tokens and sell them to the public in exchange for ETH.
However, these tokens serve a primary purpose beyond just raising funds. Utility tokens are digital assets designed for spending within a specific blockchain ecosystem. For example, Filecoin uses its token to pay users who offer data storage space. Civic pays users to verify identities and create attestations on their blockchain. Tokens are also used to create unique incentive schemes that enable people to perform specific actions within an ecosystem because they know they will be compensated. For example, token incentive models now exist that encourage people to use renewable energy. They can track and report data for energy use using IoT devices, and receive tokens as compensation through the blockchain network.
The most common type of utility token is the ERC20 Ethereum standard. Companies are able to build their decentralized applications on top of the Ethereum blockchain, and also launch their ICO’s (initial coin offerings) using ERC20 tokens.
What are Security tokens?
Security tokens are a more recent invention in the crypto space. They are considered by many to be the key to cryptocurrencies achieving mainstream adoption, due to their focus on tokenizing digital and non-digital assets, which makes them useful for almost any industry or application.
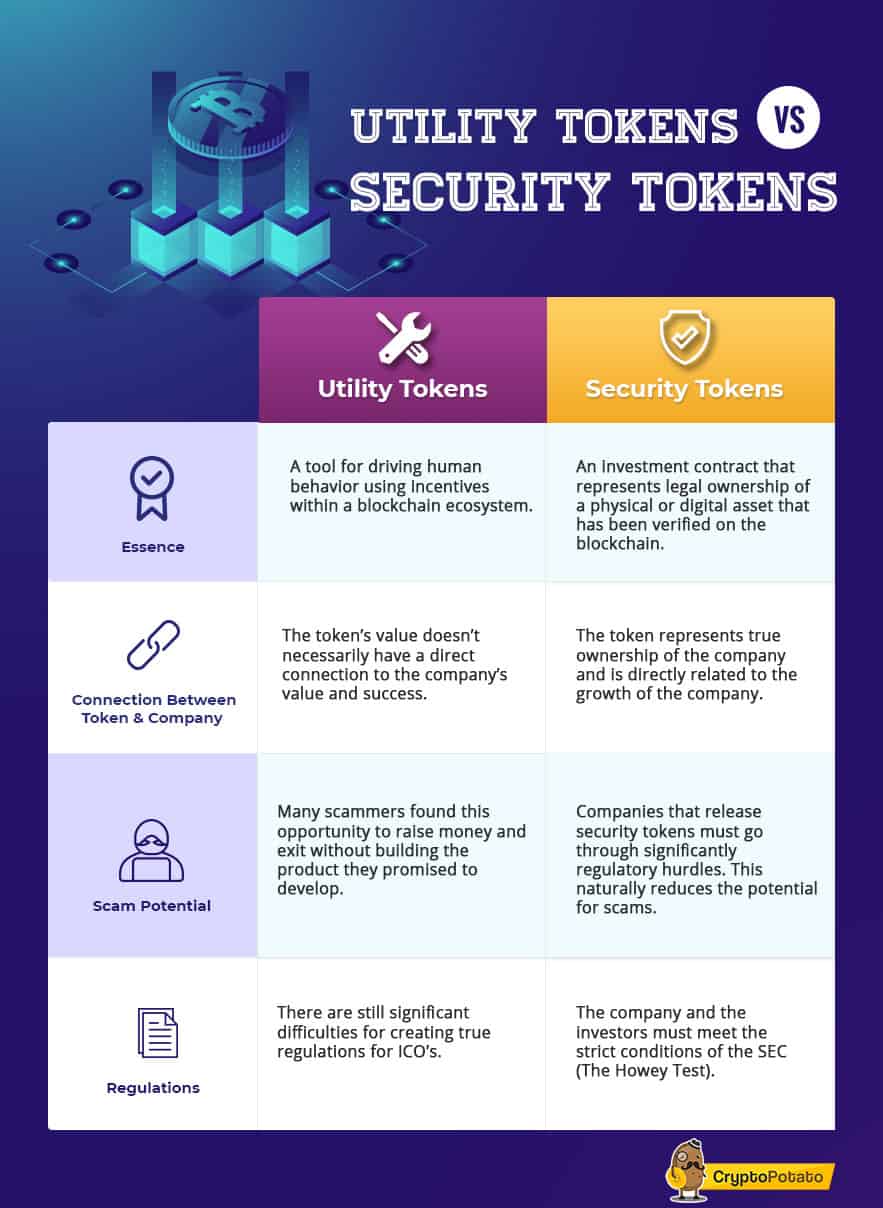
A security token is essentially an investment contract that represents legal ownership (as recognized by the SEC) of a physical or digital asset (like real estate, artwork or ETFs) that has been verified on the blockchain. Investors can exchange fiat money or cryptocurrencies for security tokens via a smart contract. With this verifiable and legal ownership, security token holders can easily trade their tokens for other assets, use them as collateral for a loan, or even fractionalize them to store in different digital wallets. The true value of security tokens is their ability to completely change how we define asset ownership, making assets that have traditionally only been available to wealthy people in developed nations more accessible to regular people all over the world to own (even if only in portions) and collect dividends from. When we think about all the physical and digital assets of the world that hold value (company equity, rewards, personal brands, etc.), and recognize that these assets can be tokenized and sold as securities on the blockchain, the possibilities for security tokens are endless.
Utility Tokens – the advantages
Utility tokens serve as a tool for driving human behavior using incentives within a blockchain ecosystem. Today, there are many challenges that our economic system is not set up to incentivize people to deal with. For example, most people would agree that people should be responsible for cleaning up the environment and using cleaner energy sources. However, under our current system, a company that sets out to clean the environment would likely have to operate as a non-profit because there is no clear business model for such an initiative.
Using blockchain technology, companies like Swytch can construct their own ecosystems, produce their own ‘money’, and use this money to incentivize people to use renewable energy. These utility tokens can be traded for Bitcoin or ETH, which can be exchanged for fiat currency, making them equally as valuable as any form of fiat money.
Utility Tokens – the disadvantages
The ease with which utility tokens can be produced has led to significant regulatory and quality assurance challenges for the crypto space. Many companies have good intentions when they launch tokens and raise funding through ICOs. However, there has also been many scams that present themselves as value-driven companies, but ultimately only seek to raise as much money as possible, then exit without building the product they promised to develop. The crypto space needs better forms of self-regulation to allow utility tokens to be seen in a more positive light.
What are the advantages of Security Tokens?
Eliminates many scams: security tokens eliminate most scams in the crypto space. Security tokens are inherently a more trustworthy investment because companies that release them have to go through significantly more regulatory hurdles before they can be accessible to the public.
Dividend payouts: Like stocks, security token investors can receive quarterly dividends paid out of the profits made from the asset they own. This provides them with a more steady and reliable income stream.
Access to multiple asset classes: security tokens offer access to any kind of company, product, fund, or structure that produces value. Security tokens significantly expand the number of options that anyone with any sum of money has to make investments.
Access to liquidity for traditionally illiquid assets: By investing in a security token that represents an ownership stake in a house, you can sell the token much faster and receive the funds almost instantly.
Access to a global network of investors: By launching a Security Token Offering (STO), startup founders or any type of creator will get access to a global pool of investors without having to launch a blockchain based business.
What are the disadvantages of Security Tokens?
Legal requirements: Securities are legally classified by the SEC under the ‘Howey Test’. The Howey test evaluates whether an asset is a security based on the following criteria:
- It is an investment of money
- There is an expectation of profits from the investment
- The money invested is in a common enterprise
- Any profit comes from the efforts of a promoter of a third party
To be classified as a security, the asset has to pass all 4 criteria.
Registering securities is no easy task, as companies must abide by a strict set of laws that require (among other things) frequent disclosure of detailed financial records in order to protect citizens from being defrauded from their investment. These requirements can be incredibly costly and time consuming for any business.
Restricted investor base: Under current US regulations, security tokens may only be available to accredited investors (i.e., investors with a $1million net worth, or $200k in annual income).
Reliably connecting real-world assets to the blockchain: there are many logistical challenges that come with tokenizing real-world assets, mainly, ensuring that the data transferred to the blockchain is both reliable and up to date. Security tokens represent trillions of dollars worth of real-world assets that will need timely and accurate data sourcing in order to determine their condition and adjust their valuation if necessary.
The post Security vs. Utility Tokens: The Complete Guide appeared first on CryptoPotato.









