Indian Rupee Slides to New Lows: A crypto opportunity?
- In 2018, the Indian Rupee declined by as much as 11% against the dollar. It now ranks as one of Asia’s worst-performing
- The main catalysts for the price decline are the high price of crude oil; the country’s account deficit, and the potential ripple effects of the US/China trade war.
A downtrend for emerging-markets
- India is just one of many emerging-market economies whose currencies are falling due to economic instability.
- Venezuela, Turkey, Argentina, Zimbabwe, Iran and India are all experiencing declines due to poorly managed central governments.
Government measures may be too little too late
- India’s Government has taken measures to improve the dollar inflow into the economy, such as easing the rules for manufacturing companies when it comes to external commercial borrowings and foreign-currency loans provided by overseas lenders
- Similar rules have also been eased for financial instruments used by Indian firms to raise overseas debt in rupees (also known as Masala Bonds).
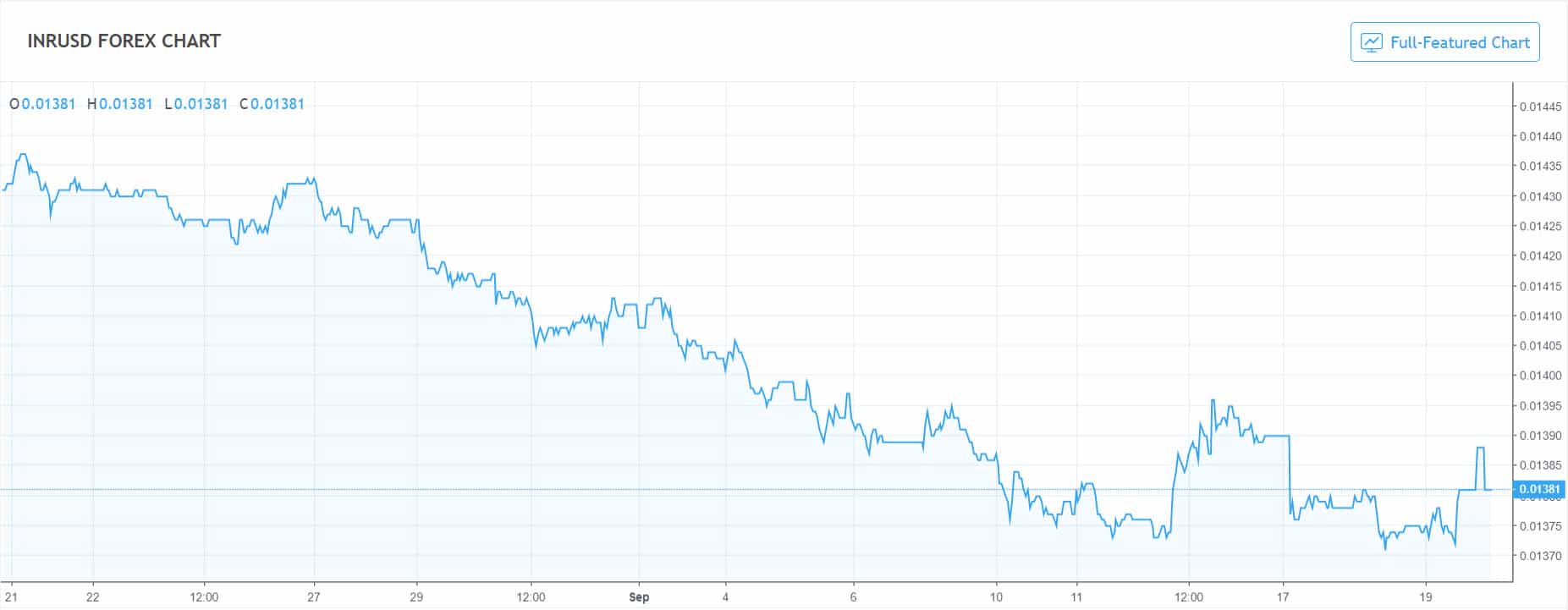
- So far, it appears as though all of these measures have had little effect in curbing the declining Rupee, which, as of today, is traded at just 72 Rupees per dollar.
Indian Government restricts alternative forms of money
- India’s government has had a history of suppressing Bitcoin adoption in the country. Crypto exchanges like BtcxIndia, Unocoin, and Coinsecure have offered their services to citizens from as early as 2013, but the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has led government crackdowns on trading that has stifled the countries innovation in the fintech
- Despite the government’s fear of Bitcoin being used by India’s citizens, they have begun to explore the potential that blockchain technology has to build a nationwide identification system (called ‘Aadhaar’) that will require fingerprint scans for food, phones, and finances. Such a program (when enhanced by blockchain technology) would only further suppress Indian citizens by restricting their access to money and monitoring their every move whether or not they were suspected of a crime.

Indian Rupee
Limited short-term impact, with more damage to come long-term
- Economic experts believe India’s current efforts to boost the value of the Rupee will only have a limited short-term impact, and may actually lead to more damage in the long-term.
“Considering that most of the measures aim at increasing short-term external debt, in effect it could worsen the risk profile of companies (by increasing unhedged exposure), and this can actually be considered negative,” said Abheek Barua, Chief Economist at HDFC Bank.
Crypto is a solution
- The growing economic troubles in India and other emerging economies are a positive sign for cryptocurrency adoption. As Governments of these emerging economies continue to reject Bitcoin as an autonomous alternative form of money, their national currencies are being replaced by cryptocurrencies via underground exchanges. For example, in 2016, Bitcoin was trading at a 25% premium in India due to such high demand. The best course of action for India would be to fully explore the utility of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as means to not only provide more economic freedom for their citizens but also to potentially create more value for the Indian economy, which could subsequently boost the value of the Rupee.
The post Indian Rupee Slides to New Lows: A crypto opportunity? appeared first on CryptoPotato.